Taylor, D., Larsen, J., Buer, A.-L., Friedland, R., Holbach, A., Petersen, J.K., Nielsen, P., Ritzenhofen, L., Saurel, C., Maar, M., 2021. Mechanisms influencing particle depletion in and around mussel farms in different environments. Ecological Indicators 122, 107304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107304
Click here or on the image to go to the document

Larsen J, Mohn C, Pastor A, Maar M (2020) A versatile marine modelling tool applied to arctic, temperate and tropical waters. PLoS ONE 15(4): e0231193. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231193
Click here or on the image to go to the document

Timmermann K, Maar M, Bolding K, Larsen J, Windolf J, Nielsen P, Petersen JK (2019) Mussel production as a nutrient mitigation tool for improving marine water quality. Aquacult Environ Interact 11:191-204. https://doi.org/10.3354/aei00306
Click here or on the image to go to the document

Per Bergström, Niklas Hällmark, Karl Johan Larsson, Mats Lindegarth (2019) Biodeposits from Mytilus edulis: a potentially high-quality food source for the polychaete, Hediste diversicolor. Aquaculture International 27, pages89–104(2019)
Click here or on the image to go to the document

Jonne Kotta, Martyn Futter, Ants Kaasik, Kiran Liversage, Merli Rätsep, Francisco R. Barboza, Lena Bergström, Per Bergström, Ivo Bobsien, Eliecer Díaz, Kristjan Herkül, Per R. Jonsson, Samuli Korpinen, Patrik Kraufvelin, Peter Krost, Odd Lindahl, Mats Lindegarth, Maren Moltke Lyngsgaard, Martina Mühl, Antonia Nyström Sandman, Helen Orav-Kotta, Marina Orlova, Henrik Skov, Jouko Rissanen, Andrius Šiaulys, Aleksandar Vidakovic, Elina Virtanen (2020) Cleaning up seas using blue growth initiatives: Mussel farming for eutrophication control in the Baltic Sea. Science of the Total Environment. Volume 709, 20 March 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136144
Click here or on the image to go to the document

Per Bergström, Ylva Durland, Mats Lindegarth (2020) Deposition of shells modify nutrient fluxes in marine sediments: effects of nutrient enrichment and mitigation by bioturbation below mussel farms. Aquaculture Environment Interactions 12:315-325
Click here or on the image to go to the document
Wouter Visch, Per Bergström, Göran M. Nylund, My Peterson, Henrik Pavia, Mats Lindegarth (2020) Spatial differences in growth rate and nutrient mitigation of two co-cultivated, extractive species: The blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) and the kelp (Saccharina latissima). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 246:107019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2020.107019
Click here or on the image to go to the document

von Thenen, M., Maar, M., Hansen, H.S., Friedland, R., Schiele, K.S., 2020. Applying a combined geospatial and farm scale model to identify suitable locations for mussel farming. Marine Pollution Bulletin 156, 111254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111254
Click here or on the image to go to the document

Maar, M., Larsen, J., Thenen, M., Dahl, K., 2020. Site selection of mussel mitigation cultures in relation to efficient nutrient compensation of fish farming. Aquaculture Environment Interactions. https://doi.org/10.3354/aei00361
Click here or on the image to go to the document

Buer, A.-L., Taylor, D., Bergström, P., Ritzenhofen, L., Klemmstein, A., 2020b. Nitrogen and Phosphorous Content in Blue Mussels (Mytilus spp.) Across the Baltic Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science 7, 705. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.00705
Click here or on the image to go to the document

Buer, A.-L., Maar, M., Nepf, M., Ritzenhofen, L., Dahlke, S., Friedland, R., Krost, P., Peine, F., Schernewski, G., 2020a. Potential and Feasibility of Mytilus spp. Farming Along a Salinity Gradient. Frontiers in Marine Science 7, 371. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.00371
Click here or on the image to go to the document
Holbach, A., Maar, M., Timmermann, K., Taylor, D., 2020. A spatial model for nutrient mitigation potential of blue mussel farms in the western Baltic Sea. Science of The Total Environment 736, 139624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139624
Click here or on the image to go to the document

Policy guidelines for implementation of mussel cultivation as a mitigation measure for coastal eutrophication in the Western Baltic Sea
Click here or on the image to go to the document

5.3 Report on site selection methods currently used for mussel farming in the Baltic Sea region
Click here or on the image to go to the document

2.5 Guideline to mediate social acceptance of the mitigation concept
Click here or on the image to go to the document

7.3 Publication on the application of ESS-tool on mussel farms and water clarity
Click here or on the image to go to the document

6.2-6.4 Production of two different meal types (with or without byssus) for fish feed; Growth of juvenile rainbow trout on processed mussel products; Digestibility of rainbow trout on processed mussel products
Click here or on the image to go to the document

6.1 Development of new cost-efficient technique for processing mussel meal.
Click here or on the image to go to the document

4.1 Maps of particle depletion around different mussel farms (in-situ, satellite, modelling) with background and explanatory information
Click here or on the image to go to the document

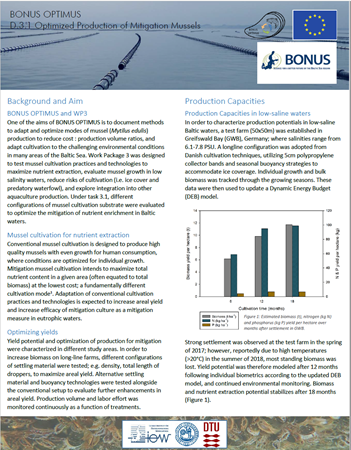
3.1 Report on Production Optimization
Click here or on the image to the link the document
Article in Frontiers
Taylor D, Saurel C, Nielsen P and Petersen JK (2019) Production Characteristics and Optimization of Mitigation Mussel Culture. Front. Mar. Sci. 6:698. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00698
Click here or on the image to the link the document

Book chapter in Goods and Services of Marine Bivalves
(Editors Aad C. Smaal, Joao G. Ferreira, Jon Grant, Jens K. Petersen, Øivind Strand)
Click here or on the image to download the full document

FACTSHEETS from the BONUS-OPTIMUS project
Click here to download the full document

EUCC’s magazine ‘Coastal & Marine’ Special ‘Blue mussel farming for improving water quality in the Baltic Sea’ (volume 2019-1), ISSN 1877-7953
The current issue of 'Coastal & Marine' informs about research results on blue mussel farming for improving water quality in the Baltic Sea.
Low salinity and harsh weather conditions have together with low regional interest in mussel products prevented a development of mussel farming in the Baltic Sea. But as the goals for environmental quality in the Baltic coastal zone have still not been met, the ecosystem services provided by mussel farming become a potential important tool for mitigation of the effects of nutrient enrichment. Combined with an increasing demand for the valuable protein source that blue mussels are both for human consumption and as a feed ingredient, mussel farming has potential also in the Baltic area.
This issue of the EUCC magazine 'Coastal & Marine' presents in a brief and popular form a synthesis of what has been already learned. Mainly based on case study sites in Denmark, Sweden and Germany the authors report on e.g. optimal production modes, how to quantify the possible positive and adverse effects of mussel farming on ecosystems and how best to integrate mussel farming into coastal maritime spatial planning.
The magazine was created by the project BONUS OPTIMUS - ‘Optimization of mussel mitigation cultures for fish feed in the Baltic Sea’ that has received funding from BONUS (Art 185), funded jointly by the EU and Baltic Sea national funding institutions.
Click here to download
